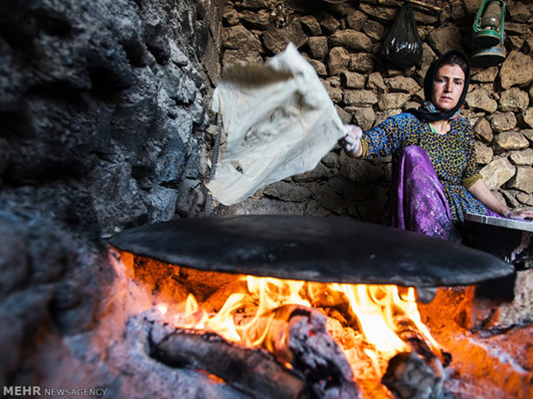The eleventh session of the Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage is underway in the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa Conference Centre in Addis Ababa, from 28 November to 2 December 2016.
During the session, UNESCO reviewed the document “Flatbread making and sharing culture: Lavash, Katryma, Jupka, Yufka” jointly submitted by Iran, Azerbaijan, Turkey, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan, and finally voted to inscribe the bread as a UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage.
The culture of making and sharing flatbread in communities of Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Turkey carries social functions that have enabled it to continue as a widely-practised tradition.
Making the bread (lavash, katyrma, jupka or yufka) involves at least three people, often family members, with each having a role in its preparation and baking. In rural areas, neighbours participate in the process together.
Traditional bakeries also make the bread. It is baked using a tandyr/tanūr (an earth or stone oven in the ground), sāj (a metal plate) or kazan (a cauldron).
Besides regular meals, flatbread is shared at weddings, births, funerals, various holidays, and during prayers. In Azerbaijan and Iran, it is put on the bride’s shoulders or crumbled over her head to wish the couple prosperity while in Turkey it is given to the couple’s neighbours.
At funerals in Kazakhstan it is believed the bread should be prepared to protect the deceased while a decision is made from God and in Kyrgyzstan sharing the bread provides a better afterlife for the deceased.
The practice, transmitted by participation within families and from master to apprentice, expresses hospitality, solidarity and certain beliefs that symbolize common cultural roots reinforcing community belonging.