Hamed Vahdati-Nasab, who headed the excavations, said, “The third season of the joint excavations by Iranian and French teams — which were conducted in cooperation with Gilles Brillon, a professor at the Museum of Anthropology in Paris — came to a close with remarkable cultural achievements.”
Vahdati-Nasab highlighted the age of the layers in this season of the excavations, saying, “In this season, the results of the dating of cultural materials at the cage, which had been sent to a laboratory at the Museum of Anthropology in Paris, show three settlements aged 160,000 210,000 and over 400,000 existed at the Qal-e Kord Cave, which makes it Iran’s most ancient archeological site.”
“In addition to the results of archeological dating, the discovery of tools, with chipping traditions older than the Middle Paleolithic era, indicates the presence of other species than humans — except the ancient intelligent man and Neanderthals — in this region,” he added.
The archeologist said the main achievement in the second season of excavations at the Qal-e Kord Cave was the discovery of teeth belonging to Neanderthal children dating back 155,000 years.
“The latest findings and the tools discovered in the cave show the cave served as a settlement for other humans that lived prior to the era of the Neanderthals, such as the Heidelberg man or other species of upright man,” Vahdati-Nasab said.
So far, two types of extinct pre-historic horses, deer, brown bear and rhino have been among the animal species discovered in the area.
Discovery of remains of a cave hyena at Iran’s most ancient archeological site
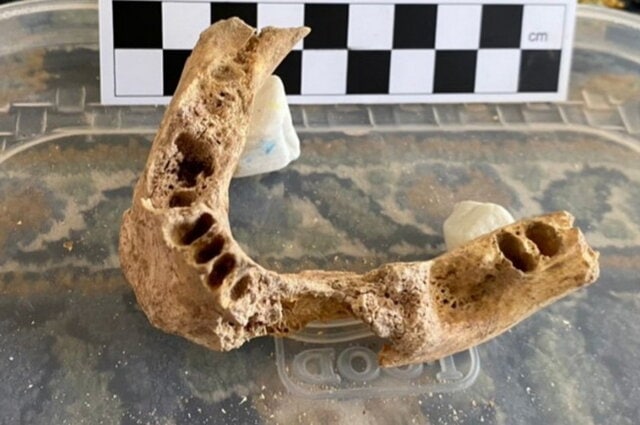
The supervisor of the excavations added that the lower jaw of modern man and the upper part of the skull of an extinct hyena, called cave hyena, which existed on earth between 11,000 to 500,000 years, were among the other discoveries in the excavations and have been reported from Iran for the first time.
The discovered materials have been handed over to the Qazvin museum for maintenance and preservation.
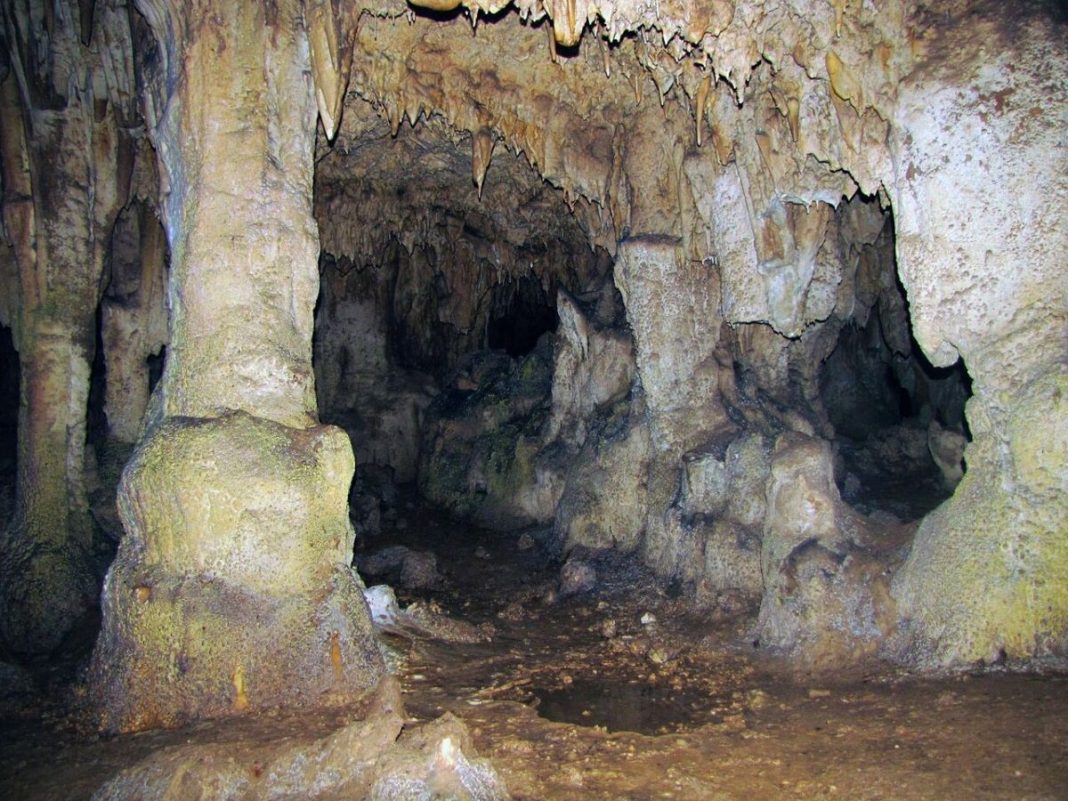
Qal-e Kord Cave, one of the oldest human settlements in Iran
According to the local cultural heritage department in Qazvin (Wikipedia), the Qal-e Kord Cave sits 20 kilometers from the Kharaqan Towers in the village of Hesar in Avaj County.
After passing through the mouth of the cave and going down a 15-meter well, a hall with an area of more than 1,000 square-meters comes into view, which has marvelously beautiful stalactites and stalagmites.
The cave is one of the oldest areas of human habitation in Iran, which is completely unique in terms of the richness of archaeological findings and human remains discovered in modern times.