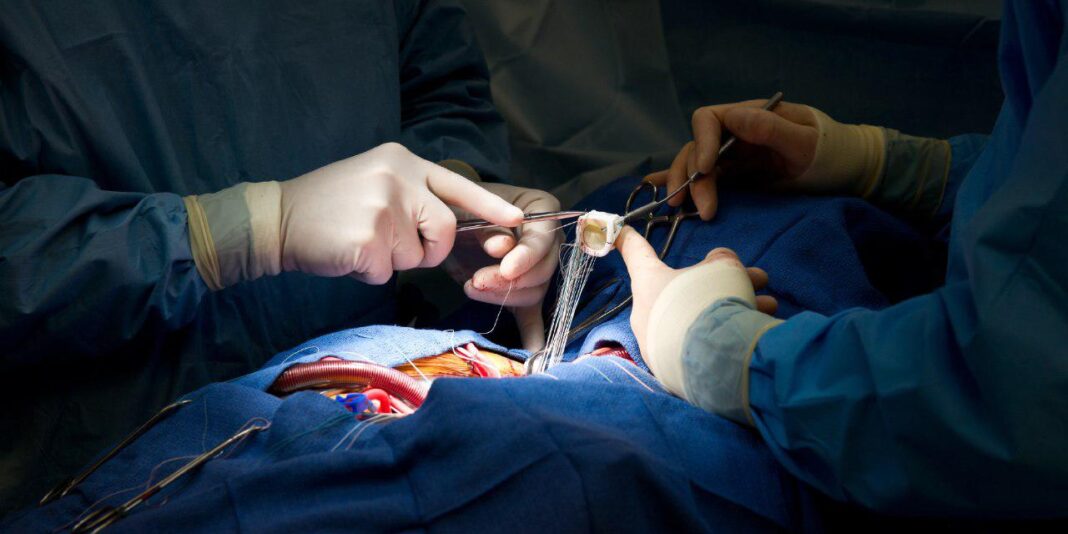
A normal heart has four chambers and as many valves which separate the chambers from each other. The valves open and close each time the heart beats.
The valves cause blood to be pumped in the right path through the atria and ventricles and other parts of the body. Any malfunction of the valves will result in serious problems for the body.
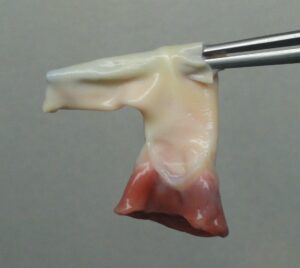
The aortic valve is located at the beginning of aorta, and the pulmonary valve is located at the beginning of the pulmonary vein.
The valves allow the blood to flow in one direction only, keeping the blood from moving in the opposite direction. The blood flows through the tricuspid valve from the left and right atria to the ventricles. When the ventricles are full of blood, the valves are closed.
The closure of the valves keeps the flood flowing from the ventricles to the atria. When the ventricles contract, the aortic and pulmonary valves open whereby blood is pumped out of the ventricles.
While the heart is contracting, blood enters the left ventricle from the left atrium through the mitral valve before being pumped into the whole body. The blood being pumped contains oxygen. Oxygen transfer takes place between blood and tissues.
The blood loses oxygen and takes in CO2. When the heart is relaxing, oxygen-depleted blood returns from the whole body to the right atrium from where it is pumped to the lungs via the tricuspid valve to receive oxygen.
Diseases and Replacement
There are some diseases which affect heart valves. One such disease is valve prolapse which causes blood to flow back into the heart. This condition happens when the valve does not close tightly.
For a brief review of Iran’s achievements in various fields of science and technology, check the book “Science and Technology in Iran: A Brief Review”
When tissues of heart valves become thick or blocked, it will result in a condition called stenosis. In this condition, valves do not open enough and block blood flow.
Sometimes heart valves are completely blocked and there is no way for blood to flow.
The treatment of heart valves depends on the state and intensity of the disease. Many people suffering from heart valve diseases continue to live for a long time and never need to undergo heart valve replacement surgery.
However, if the heart valve disease negatively affects the ability to pump blood, then the valve will likely need to be repaired or replaced or be operated on.